/
Page Settings
Last updated:
Quick Start:
- Page Name vs Page Title: Use a short, admin-friendly Page Name for management, and a descriptive Page Title for users and SEO.
- Page Type: Use Standard Page for fixed content; CMS Detail Page for dynamic content driven by CMS.
- URL Path: Use semantic, hierarchical paths for SEO (
/about,/blogs/:slug). - Published Status: Keep pages unpublished while under construction; publish when ready.
In the editor, go to the left-hand Pages panel and click the three dots next to a page to access Page Settings.
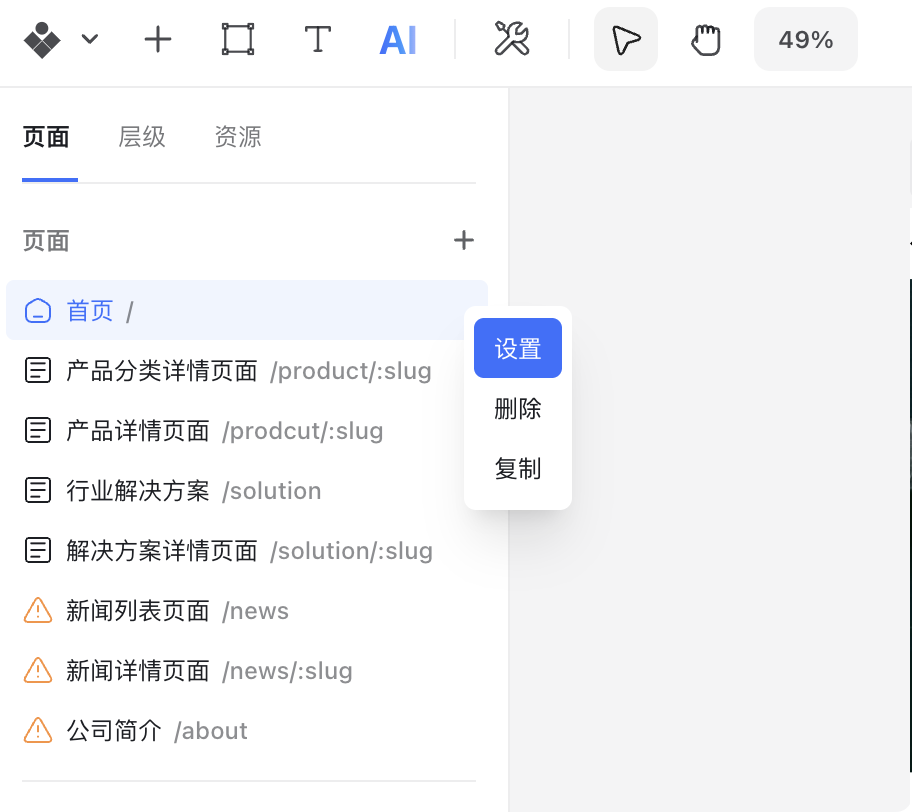
In Page Settings, you can configure the following: page path (URL), page type, published status, and SEO settings.
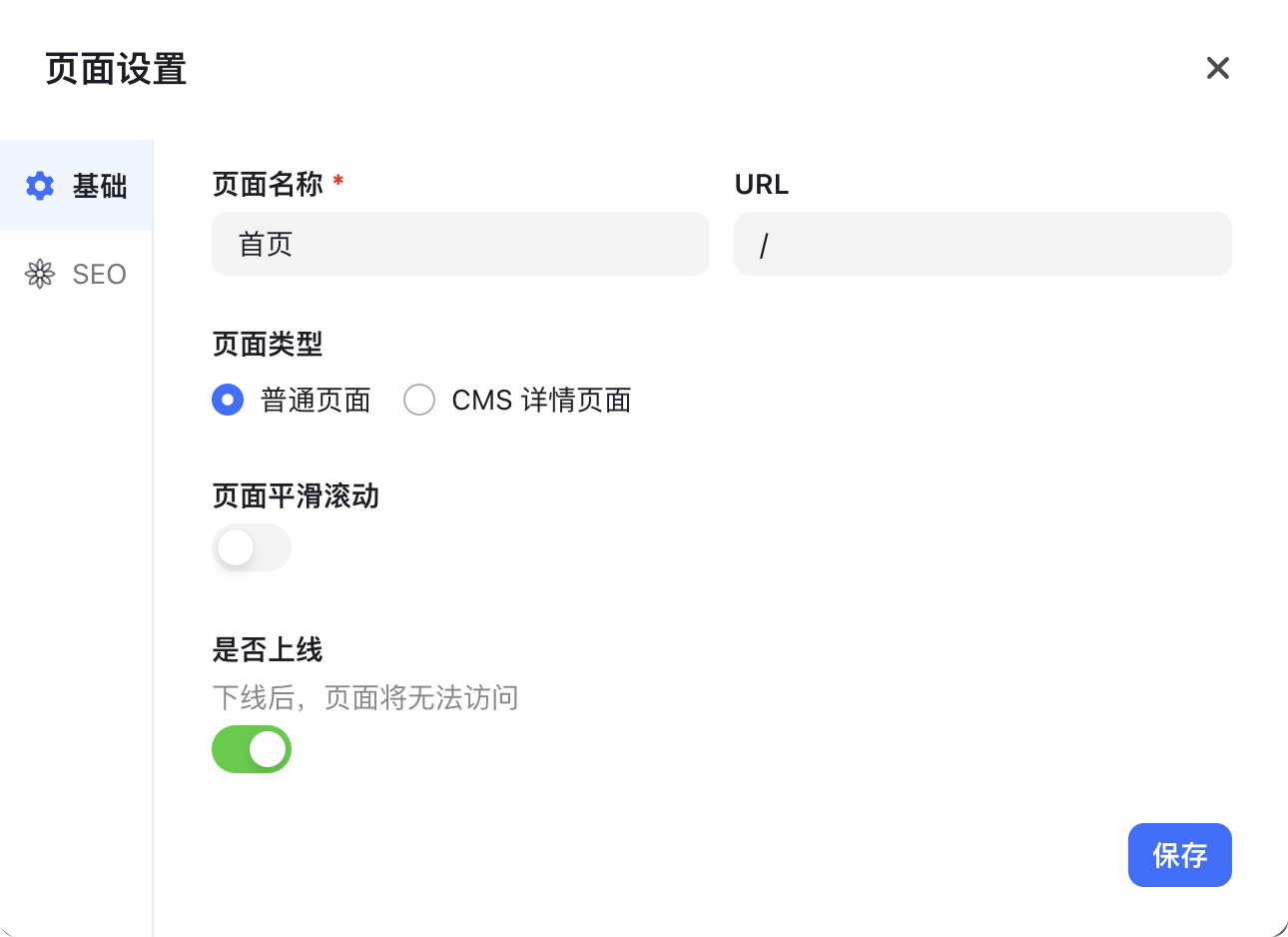
Page Name
The Page Name is primarily for the website administrator to distinguish pages in the editor—it is not visible to users.
Example:
- Page Title (visible to users & SEO): “Durable and Easy-to-Use Hardware | XX Hardware”
- Page Name (for management): “Home”
For more on SEO, see: SEO Settings
URL Path
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of your page on the web. Think of it as a "house number" that tells the browser where to find your content.
Example: If the page URL path is /blogs, users can access it via:https://{your-domain}/blogs
Special URL Rules
- Home Page: Set path to
/. - Custom 404 Page: Set path to
/404to display when users visit a non-existent page. - Unique Paths: URL paths must be unique. If a path already exists, change the existing page’s path first (e.g.,
/index-old).
Semantic URLs improve SEO and user experience.
Simple Guidelines
- Use meaningful words: e.g., About Us →
/about, Contact →/contact - Maintain correct hierarchy: e.g.,
/blogs/about-creght
URL Variable – Slug
For CMS Detail Pages, there is no fixed URL. For multiple dynamic pages (like blogs), use a slug variable:
/blogs/:slug
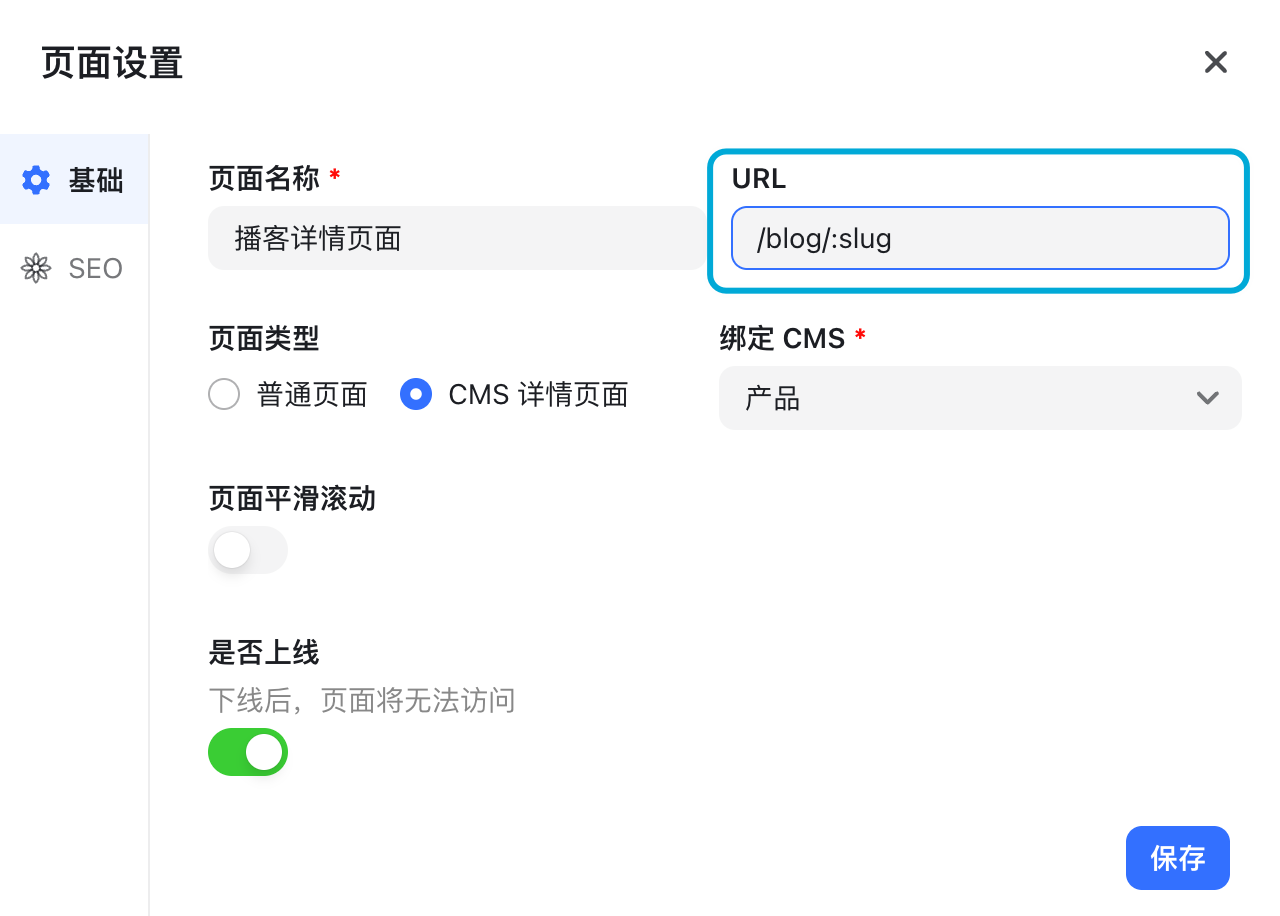
Combine this with the slug field in your CMS to generate dynamic URLs.
Page Type
There are two types of pages:
- Standard Page: Fixed URL, e.g., Home, About Us.
- CMS Detail Page: Displays dynamic CMS content using one layout. Examples: blog posts, news, case studies.
The main difference is that CMS Detail Pages must be linked to a CMS:
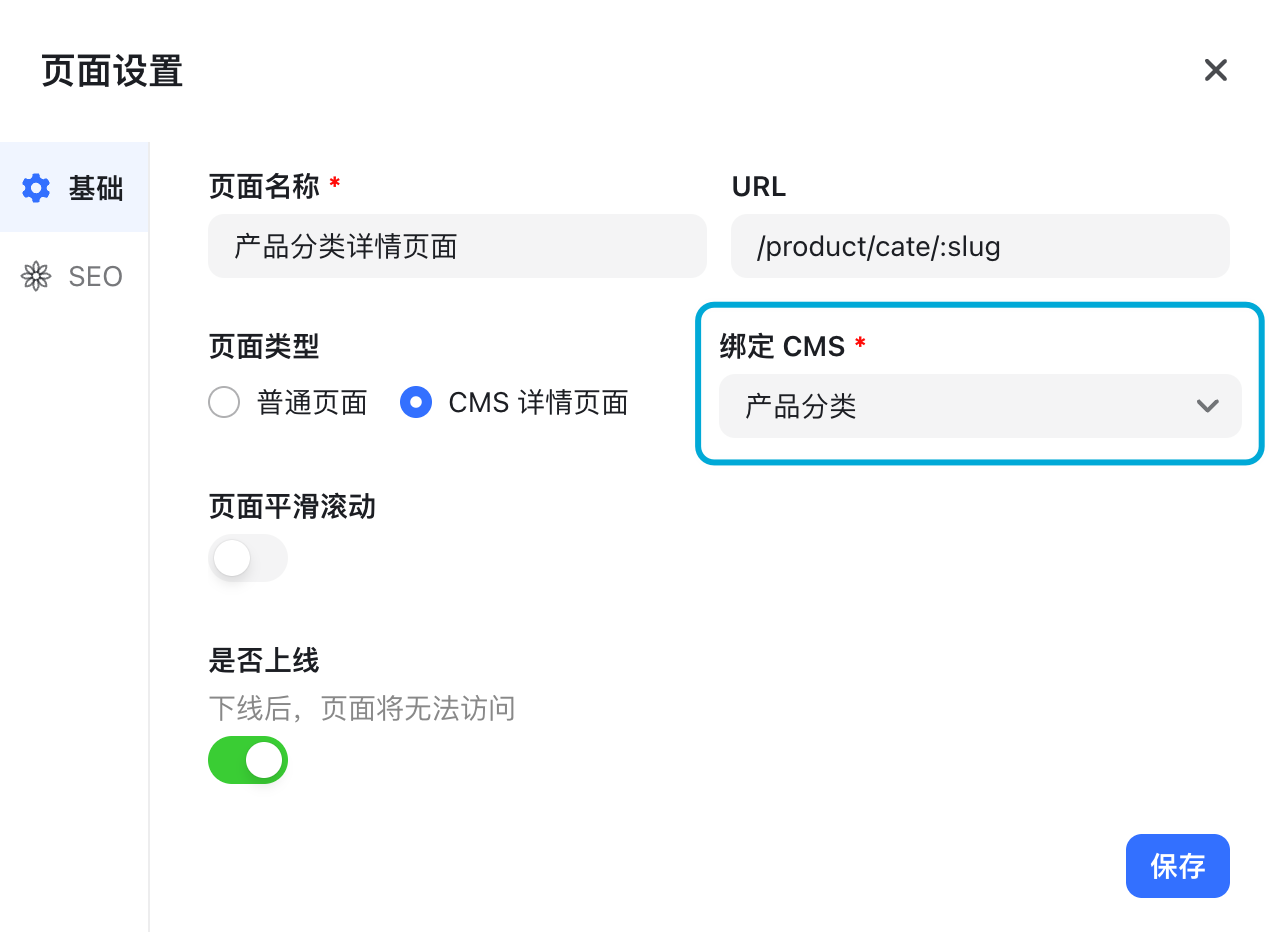
Components like images or text can then bind to the selected CMS fields.
For more on CMS, see: Content Management – CMS
Smooth Scrolling
Enable Smooth Scrolling to achieve a smoother scrolling experience using the plugin. You can toggle this feature on or off to compare the difference.
Published Status
By default, new pages are published. Once the website is live, the page is accessible to users.
Switch a page to unpublished to hide it from users and search engines—useful for pages still under construction.
SEO
For detailed SEO settings, see: SEO Settings
.png?w=3072&fmt=webp)