Design
/
Position in Creght
Last updated:
2025-08-27
Creght supports four types of positioning: Relative, Absolute, Fixed, and Sticky.
You can change an element’s positioning in the right-hand settings panel.
i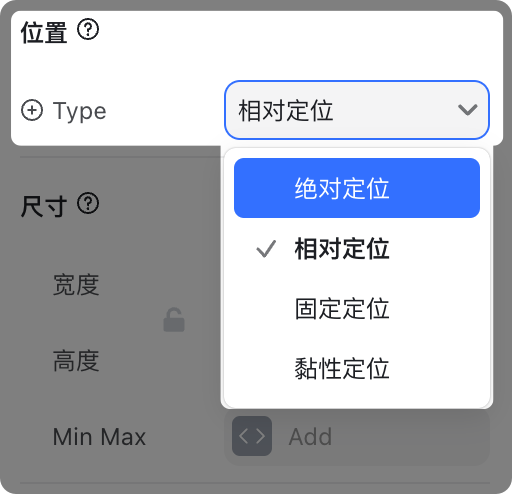
1. Relative Positioning
- Default positioning for all elements
- ✅ Stays in the document flow (occupies space)
- Parent containers with auto width/height will not collapse
- Elements are arranged in order, without overlap

2. Absolute Positioning
- ❌ Removed from the document flow (does not occupy space)
- Parent containers with auto width/height will collapse
- Elements can overlap with others

When Absolute is selected, a Position Controller appears:

This allows precise placement of an element relative to its parent (e.g., bottom: 0, left: 0).
Use cases:
- Overlaying elements (e.g., badges, icons on images)
- Manual placement inside containers

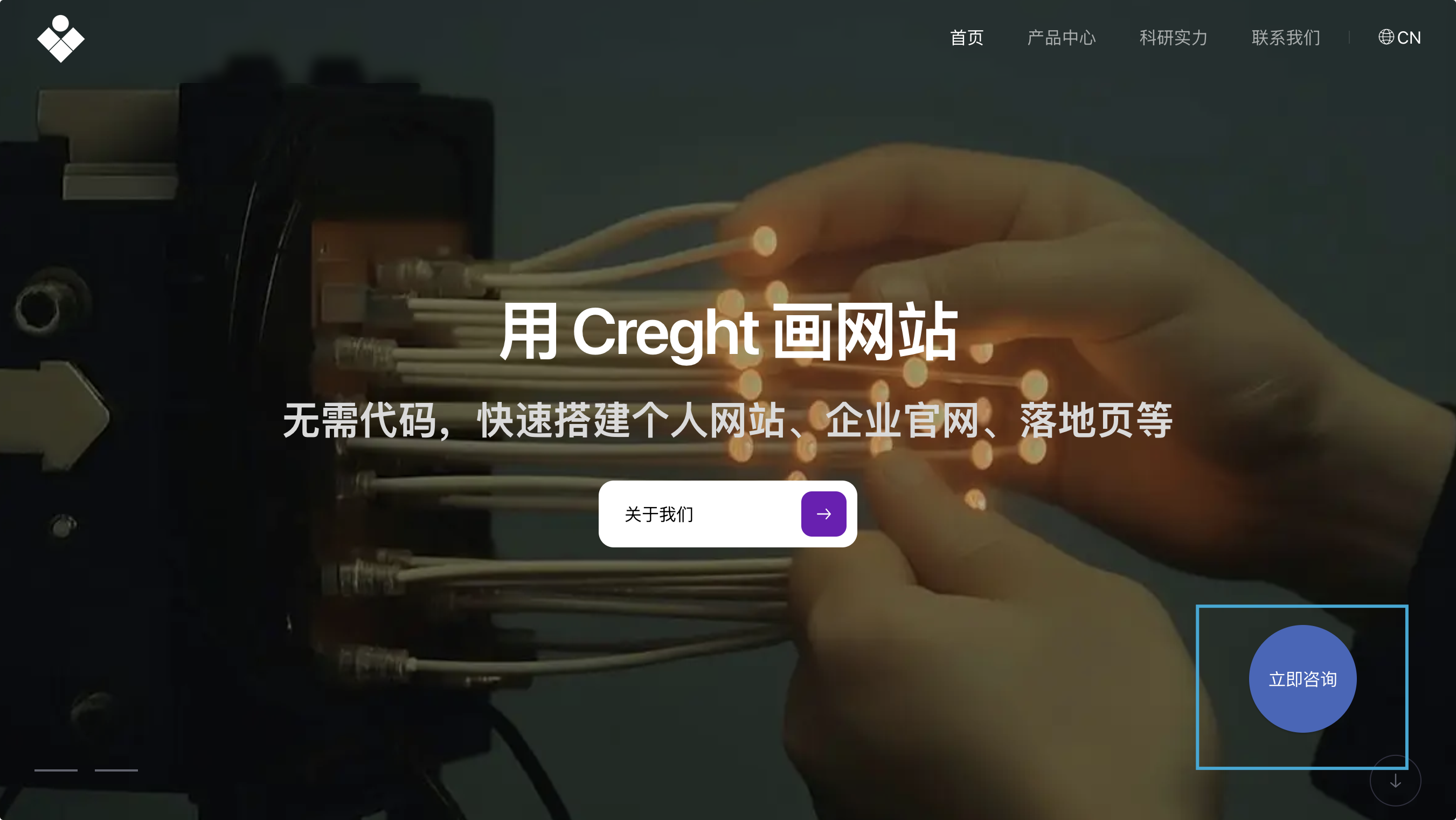
3. Fixed Positioning
- ❌ Removed from document flow (does not occupy space)
- Pinned relative to the browser viewport
- Example:
top: 0keeps the element fixed to the top, even when scrolling
Use cases:
- Persistent navigation bars
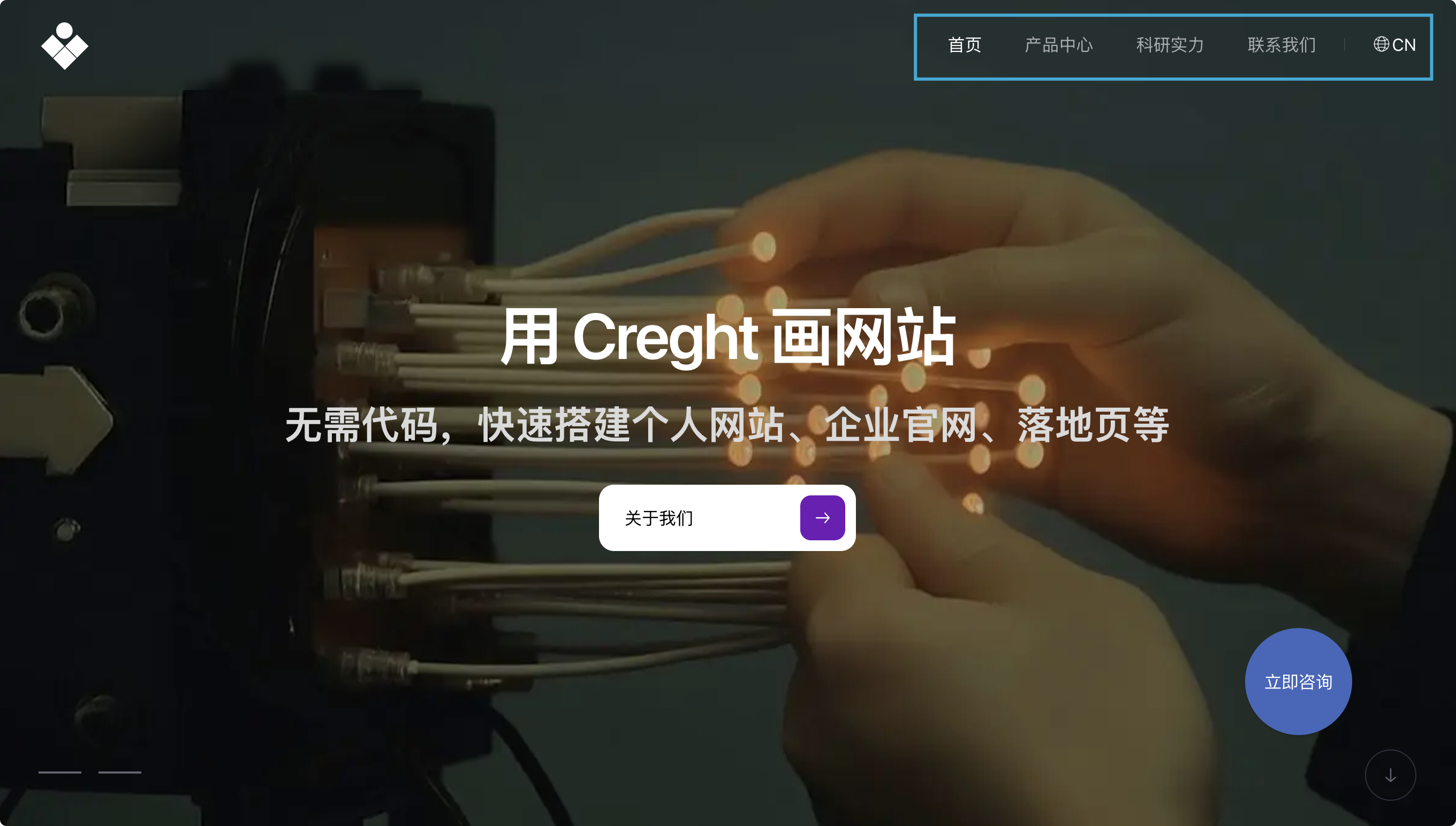
- Floating “Contact Us” / “Chat Now” buttons
4. Sticky Positioning
- ✅ Remains in the document flow (occupies space)
- Acts as Relative until a threshold is reached, then switches to Fixed
- Great for elements that should “stick” temporarily while scrolling
👉 Try it yourself: Sticky Positioning Demo
Position Comparison
| Positionin | In Document Flow | Occupies Space | Moves with Scroll | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Default positioning, normal flow |
| Absolute | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (relative to parent) | Overlays, manual placement |
| Fixed | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No (fixed to viewport) | Nav bars, floating buttons |
| Sticky | ✅ Yes (until threshold) | ✅ Yes | Mixed (Relative → Fixed) | Section headers, sticky cards |
✅ Summary:
- Use Relative for default layouts
- Use Absolute for overlays inside a parent
- Use Fixed for elements pinned to the screen
- Use Sticky for hybrid scroll-based behaviors
.png?w=3072&fmt=webp)